Understanding the metal free zone of Fanchi-tech Metal Detector(MFZ)
Frustrated with your metal detector rejecting for no apparent reason, causing delays in your food production? The good news
is there might be a simple way to avoid such occurrences. Yes, learn about the Metal Free Zone (MFZ) to easily ensure your
line runs trouble free.
What is a metal free zone?
Metal detectors are designed so the detector’s high frequency magnetic field is contained within the metal casing of the
device. Despite this there is the possibility of some magnetic field leakage from the aperture of the detector. Known as the
MFZ, this area surrounding the metal detector's aperture should be kept free of any fixed or moving metal to prevent any
false rejects. It is important to be aware of the MFZ, as several calls a week received by FANCHI’S Technical Department are
a result of metal in this zone.
What are symptoms of metal in the MFZ?
If you place metal too close to a metal detector, (i.e. in the MFZ) the signal will spike, leading to false rejects and disrupting
the production line. This can appear to be random or follow a pattern, it will depend on what type of encroachment is
causing the issue (moving or non-moving metal). It can also produce symptoms like that of a contaminated belt or phone
use.
How do I ensure I have a Metal Free Zone?
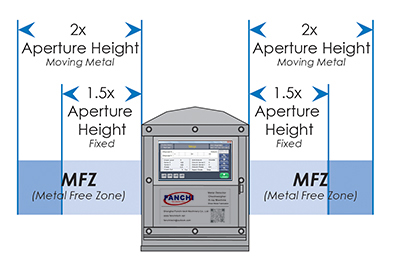
To ensure you have a MFZ, you’ll need to know how to calculate it. The calculation varies depending on two key factors;
is it moving or non-moving metal. It is suggested fixed metal must have a distance from the aperture opening of 1.5x
aperture height and moving metal a distance of 2.0 x aperture height. The only exception to this rule is gravity fed
systems that are integrated into fill and seal baggers with a chute going through the aperture. These units are normally
built with either welded or bolt-on rings, keeping the field aimed up the chute, preventing it from spreading to the structure
and causing instability.
Non-moving metal
Examples of non-moving metal includes; Conveyor covers, factory fixtures, other production lines, etc.
Calculation – 1.5 x the aperture height. For example, if the aperture height is 200mm, multiply by 1.5, meaning the MFZ
will be 300mm from the edge of the metal detector aperture.
Moving metal
Examples of moving metal includes; rollers, motors, personal items such as keys, etc.
Calculation – 2 x the aperture height. For example, if the aperture height is 200mm in height, multiply by 2.0, meaning the MFZ will be
400mm from the edge of the metal detector aperture.
Note: The top, back and bottom of the head do not need a certain distance due to the steel casing blocking the signals.
However, you can look to use 1 x the aperture height, but this will not be true for large heads. The figures above are based
on a general rule for the Fanchi-tech Conveyorised Metal Detector.
